Is your WordPress site moving slower than a snail in molasses? You’re not alone. In 2025, with Google’s Core Web Vitals playing a crucial role in search rankings and user attention spans dropping to just 8.25 seconds, website speed isn’t just nice-to-have—it’s make-or-break for your business.
Here’s a wake-up call: studies show that a mere one-second delay in page load time can slash your conversions by 7%. That’s not a typo. Meanwhile, 53% of mobile users abandon sites that take longer than 3 seconds to load. If your WordPress site isn’t optimized for speed, you’re literally watching money walk out the door.
But here’s the good news—you don’t need to be a tech wizard to dramatically improve your site’s performance. In this comprehensive guide, I’ll walk you through 15 proven WordPress performance optimization tips that have helped thousands of websites achieve lightning-fast loading speeds and better search rankings.
Why WordPress Performance Matters More Than Ever in 2025
Before we dive into the technical stuff, let’s talk about why this matters. The data is crystal clear:
- Conversion Impact: Sites that load in 1 second convert 3 times more than sites that load in 5 seconds (Portent study)
- Revenue Impact: SpeedSense helped an e-commerce company achieve a 7.6% increase in sitewide conversion, translating to roughly $6 million in annual revenue
- SEO Impact: Google and other search engines actively penalize slower websites by pushing them down in search results
- User Experience: Mobile transactions increased by nearly 30% for businesses that prioritized speed optimization
The bottom line? Speed optimization isn’t just about making your site faster—it’s about making your business more profitable.
1. Choose Quality WordPress Hosting (The Foundation of Speed)
Let’s start with the elephant in the room: your hosting provider. You can optimize plugins, compress images, and implement every trick in the book, but if your hosting is slow, your site will be slow. Period.
In 2025, there’s honestly no excuse for using budget hosting providers like Bluehost, GoDaddy, or HostGator. The price difference between excellent hosting and horrible hosting is negligible, but the performance difference is massive.
What to Look For in WordPress Hosting:
- SSD Storage: Solid State Drives are non-negotiable
- HTTP/2 Support: Enables faster loading of multiple resources
- PHP 8.1+ Support: Newer PHP versions are significantly faster
- Built-in Caching: Server-level caching beats plugin caching every time
- CDN Integration: Content delivery networks for global speed
Pro Tip: Managed WordPress hosting providers like WP Engine have shown an average site speed improvement of 68% compared to shared hosting. Yes, it costs more, but the ROI in speed and reduced maintenance makes it worth every penny.
Hosting Provider Comparison Table
| Hosting Provider | Starting Price | Performance Rating | Server Response Time | PHP Version | Built-in Caching | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WP Engine | $20/month | 9.5/10 | Under 200ms | PHP 8.2 | Yes | Business sites |
| Kinsta | $35/month | 9.7/10 | Under 150ms | PHP 8.2 | Yes | High-traffic sites |
| SiteGround | $2.99/month | 8.5/10 | Under 350ms | PHP 8.1 | Yes | Small businesses |
| Bluehost | $2.95/month | 6.0/10 | 600-1200ms | PHP 7.4 | Basic | Beginners only |
| GoDaddy | $5.99/month | 5.5/10 | 800-1500ms | PHP 7.4 | No | Not recommended |
2. Implement Caching (The Low-Hanging Fruit)
WordPress is dynamic by default, meaning every page visit triggers PHP and MySQL to generate the page from scratch. Caching creates static versions of your pages, serving them instantly to visitors without all that backend processing.
Think of it like this: instead of cooking a meal from scratch every time someone orders, you prep meals in advance and just heat them up. The end result is the same, but it’s infinitely faster.
Types of Caching to Implement:
- Page Caching: Stores complete HTML versions of your pages
- Browser Caching: Tells browsers to store certain files locally
- Object Caching: Caches database queries and complex operations
Caching Plugin Comparison Table
| Plugin | Price | Page Caching | Database Caching | Minification | CDN Support | Ease of Use | Performance Impact |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WP Rocket | $59/year | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | 9/10 | 40-60% faster |
| LiteSpeed Cache | Free | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | 7/10 | 50-70% faster |
| W3 Total Cache | Free/$99/year | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | 6/10 | 30-50% faster |
| WP Super Cache | Free | Yes | No | No | No | 8/10 | 20-35% faster |
Critical Warning: Never install two caching plugins. That’s like hiring two chefs for the same meal—you’ll get a mess, not speed.
3. Optimize Your Images (The Biggest Speed Killer)
Images typically comprise about 50% of a web page’s file size. A single unoptimized image can slow down your entire site more than a dozen poorly coded plugins combined.
The Three-Step Image Optimization Process:
Step 1: Resize Before Upload
Don’t upload a 4000×3000 pixel image if you’re only displaying it at 800×600. Resize images to their actual display size before uploading.
Step 2: Compress Without Quality Loss
Use compression to reduce file size while maintaining visual quality. Tools like Optimole or ShortPixel can automate this process.
Step 3: Convert to Modern Formats
WebP images are 25-35% smaller than JPEGs with the same quality. In 2025, WebP support is nearly universal, so there’s no reason not to use it.
Lazy Loading: Load Images Only When Needed
Lazy loading delays loading images until they’re about to enter the user’s viewport. This dramatically improves initial page load times, especially on image-heavy pages.
The good news? WordPress has built-in lazy loading since version 5.5. But for enhanced control, consider plugins like Lazy Load by WP Rocket or a3 Lazy Load.
4. Audit and Optimize Your Plugins
Here’s a harsh truth: most WordPress performance issues stem from poorly coded or unnecessary plugins. Every plugin adds weight to your site, and some are absolute performance killers.
The Plugin Audit Process:
1. Take Inventory
List every active plugin and ask: “Do I actually need this?” You’d be surprised how many plugins you forgot about or no longer use.
2. Deactivate and Test
Temporarily deactivate all plugins and test your site speed. Then reactivate them one by one, testing speed after each activation. You’ll quickly identify the culprits.
3. Find Alternatives
If a plugin is slowing you down, look for lighter alternatives or built-in WordPress solutions. For example, many sites use heavy social sharing plugins when simple HTML buttons work just as well.
Performance Testing Tool: The Query Monitor plugin is invaluable for identifying slow database queries and plugin performance issues.
5. Leverage Content Delivery Networks (CDNs)
A CDN stores copies of your static files (images, CSS, JavaScript) on servers around the world. When someone visits your site, they receive files from the server closest to them, dramatically reducing load times.
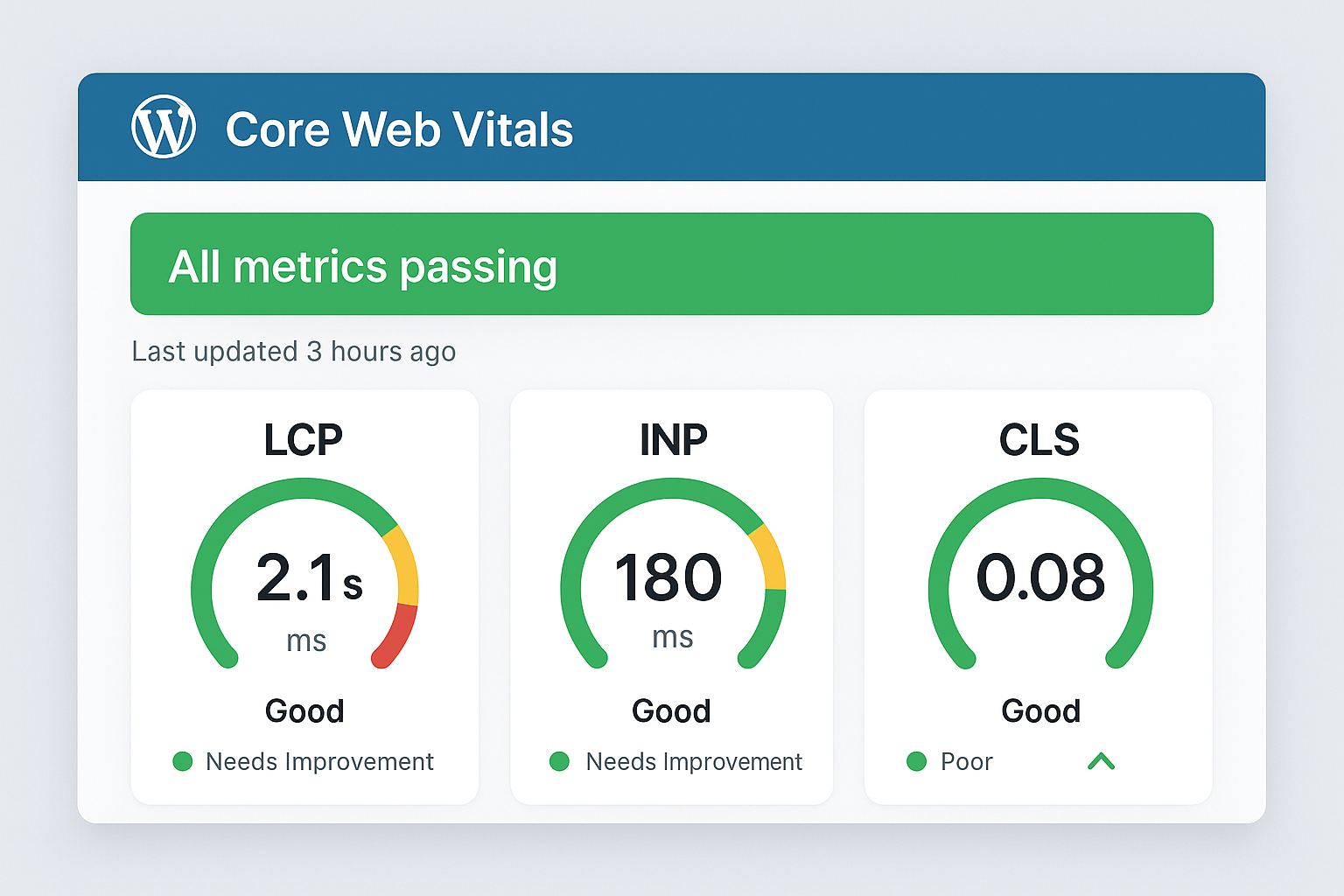
CDN Options for 2025:
For example, if your site is hosted in New York but someone visits from Tokyo, a CDN serves files from a server in Asia rather than forcing a round trip to New York.
- Cloudflare: Free tier available, excellent global coverage
- MaxCDN (StackPath): Fast and affordable
- AWS CloudFront: Powerful but more complex setup
Many caching plugins integrate seamlessly with CDNs, making setup a breeze.
6. Optimize Your Database
Your WordPress database is like a filing cabinet. Over time, it accumulates junk: spam comments, post revisions, trashed content, and expired transients. This clutter slows down database queries and, consequently, your site.
Database Optimization Checklist:
- Remove Spam Comments: Delete spam and pending comments
- Limit Post Revisions: WordPress saves every draft—limit this to 3-5 revisions
- Clean Expired Transients: Remove temporary data that’s no longer needed
- Optimize Database Tables: Like defragmenting a hard drive
Plugin Recommendation: WP-Optimize handles all of this automatically, with options to schedule regular cleanups.
Real-World Impact: A WP Engine study found that websites with optimized databases loaded up to 2x faster than those with unoptimized databases.
7. Minify and Compress CSS/JavaScript
Minification removes unnecessary characters from code files (spaces, comments, line breaks) without changing functionality. It’s like removing all the fluff from a sentence while keeping the meaning intact.
Compression (GZIP) further reduces file sizes by up to 70%. Combined, these techniques can significantly reduce the amount of data transmitted to users’ browsers.
What to Minify:
- CSS Files: Stylesheet code
- JavaScript Files: Interactive functionality code
- HTML: Page markup (be careful with this one)
Most caching plugins handle minification automatically. WP Rocket, Autoptimize, and Fast Velocity Minify are excellent options.
8. Optimize Core Web Vitals
Google’s Core Web Vitals are three specific metrics that measure user experience and directly impact search rankings:
Core Web Vitals Metrics Table
| Metric | What It Measures | Good Score | Needs Improvement | Poor Score | Common Issues | Quick Fixes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) | Loading performance | ≤ 2.5s | 2.5s – 4.0s | > 4.0s | Large images, slow server | Optimize images, upgrade hosting |
| Interaction to Next Paint (INP) | Interactivity responsiveness | ≤ 200ms | 200ms – 500ms | > 500ms | Heavy JavaScript, blocking resources | Minimize JS, remove unused code |
| Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS) | Visual stability | ≤ 0.1 | 0.1 – 0.25 | > 0.25 | Images without dimensions, web fonts | Set image dimensions, optimize fonts |
Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) – Target: Under 2.5 seconds
Measures how long it takes for the largest content element to load. Usually, this is your hero image or main heading.
Optimization Tips:
- Optimize your largest images
- Use proper image sizing and formats
- Implement preloading for critical resources
Interaction to Next Paint (INP) – Target: Under 200ms
Measures how quickly your site responds to user interactions like clicks and taps.
Optimization Tips:
- Minimize JavaScript execution time
- Remove unused JavaScript
- Optimize third-party scripts
Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS) – Target: Under 0.1
Measures how much content shifts around as the page loads. Ever clicked a button only to have it move at the last second? That’s poor CLS.
Optimization Tips:
- Define image and video dimensions
- Reserve space for ads and dynamic content
- Use proper font loading strategies
Test your Core Web Vitals scores with Google PageSpeed Insights and get detailed optimization recommendations.
9. Reduce HTTP Requests
Every resource on your page (images, stylesheets, scripts) requires a separate HTTP request. More requests = slower loading. It’s like ordering individual items from a restaurant versus ordering a combo meal—the combo is always faster.
Strategies to Reduce HTTP Requests:
- Combine CSS Files: Merge multiple stylesheets into one
- Combine JavaScript Files: Bundle scripts together
- Use CSS Sprites: Combine small images into one file
- Inline Critical CSS: Include essential styles directly in HTML
Many performance plugins handle file combination automatically, but be careful—sometimes it can break functionality. Always test thoroughly.
10. Implement Preloading Strategies
Preloading tells the browser to fetch certain resources before they’re actually needed. It’s like having your coffee order ready before you reach the counter.
Types of Preloading:
- DNS Prefetch: Resolves domain names in advance
- Preconnect: Establishes connections to external domains
- Resource Preload: Fetches critical resources early
- Page Prefetch: Loads likely next pages in the background
WP Rocket and other performance plugins offer easy preloading configuration.
11. Optimize WordPress Heartbeat API
The WordPress Heartbeat API keeps the connection between your browser and server alive, enabling real-time features like auto-save and notifications. However, it can also cause high admin-ajax.php usage and slow down your site.
Heartbeat Optimization Settings:
- Dashboard: Reduce frequency to 60 seconds (default is 15)
- Post Editor: Keep at 15 seconds for auto-save functionality
- Frontend: Disable completely unless needed
The Heartbeat Control plugin makes these adjustments simple and safe.
12. Choose a Lightweight Theme
Your theme is the foundation of your site’s design and performance. A bloated theme can undo all your optimization efforts, while a well-coded theme enhances them.
What Makes a Theme Fast:
- Clean Code: Well-structured, efficient programming
- Minimal HTTP Requests: Fewer external resources
- Mobile Optimization: Responsive design that loads quickly on all devices
- Limited Features: Focused functionality rather than kitchen-sink approach
Fast Theme Recommendations:
- GeneratePress: Lightweight and highly customizable
- Astra: Fast-loading with extensive options
- Neve: Modern and performance-focused
13. Update PHP and WordPress Regularly
This sounds basic, but it’s crucial. Newer versions of PHP and WordPress aren’t just about new features—they’re significantly faster and more secure.
The Numbers Don’t Lie:
- PHP 8.1 is up to 50% faster than PHP 7.4
- WordPress 6.4 includes numerous performance improvements over previous versions
- Security updates protect against vulnerabilities that could slow or crash your site
Best Practice: Test updates on a staging site first, but don’t delay updates indefinitely. The performance and security benefits far outweigh the risks.
14. Monitor and Troubleshoot Performance Issues
Performance optimization isn’t a one-time task—it’s an ongoing process. Regular monitoring helps you catch issues before they impact users and identify new optimization opportunities.
Essential Monitoring Tools:
- Google PageSpeed Insights: Free tool with Core Web Vitals data
- GTmetrix: Detailed performance analysis and recommendations
- Pingdom: Regular monitoring with alerts
- Query Monitor: WordPress plugin for debugging performance issues
What to Monitor:
- Page Load Times: Track changes over time
- Core Web Vitals: Google’s ranking factors
- Server Response Times: TTFB (Time to First Byte)
- Error Rates: 404s and server errors
Pro Tip: Set up alerts for performance degradation. It’s better to catch issues early than to discover them when users complain.
15. Advanced Optimization: Object Caching and Server-Level Tweaks
For sites with high traffic or complex functionality, advanced optimization techniques can provide significant performance gains.
Object Caching
Object caching stores database query results in memory, eliminating the need to re-run expensive queries. Redis and Memcached are popular solutions that can dramatically speed up dynamic content.
Server-Level Optimizations
- HTTP/2: Enables multiplexing for faster resource loading
- GZIP Compression: Reduces file transfer sizes
- Opcache: Caches compiled PHP code
- Database Query Optimization: Index optimization and query tuning
These optimizations typically require server access or managed hosting that includes them by default.
Real-World Performance Results
Let’s look at some concrete examples of what proper WordPress optimization can achieve:
Case Study 1: E-commerce Site
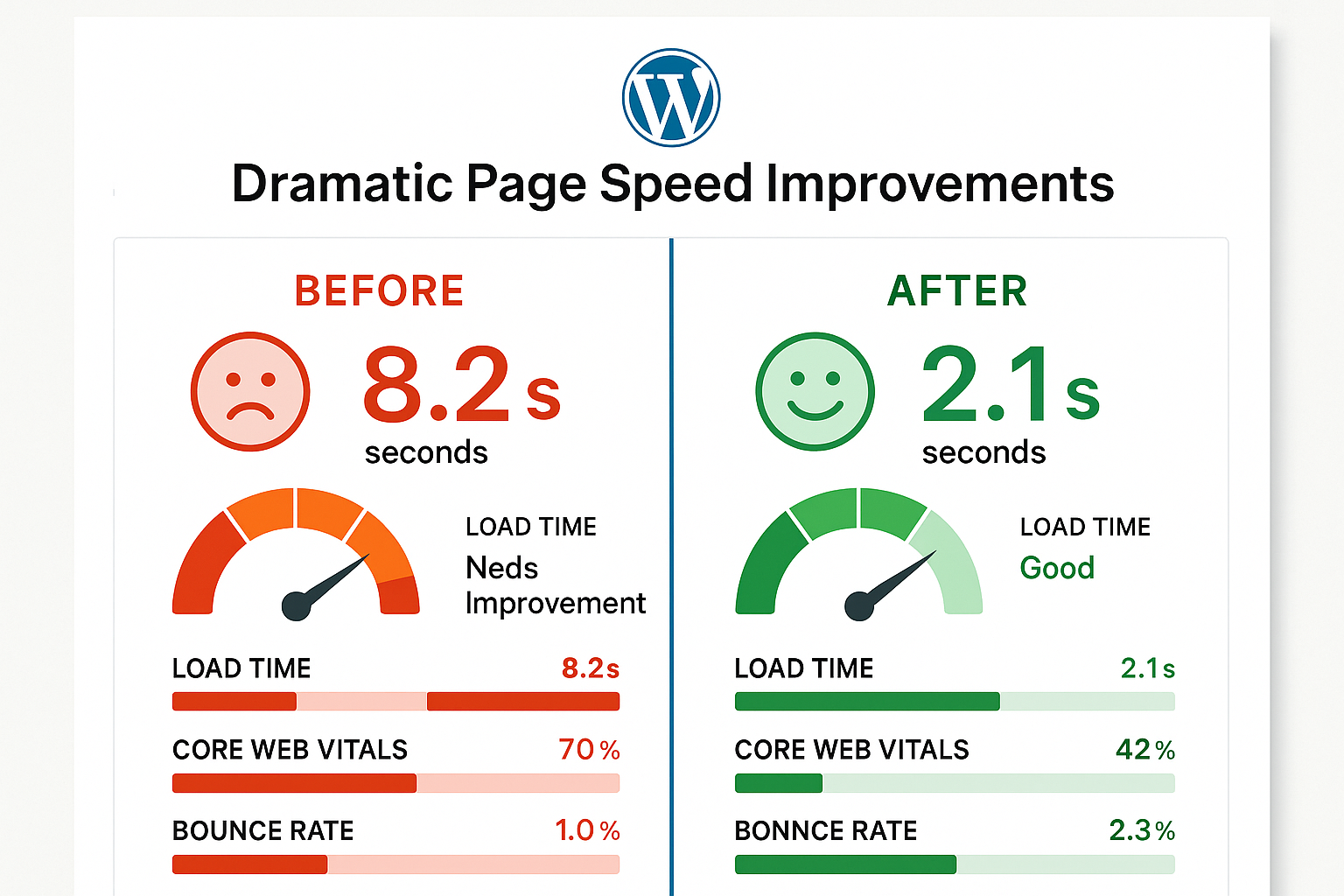
A small business e-commerce site was struggling with 8-second load times on shared hosting. After implementing these optimizations:
- Upgraded to managed WordPress hosting
- Implemented WP Rocket caching
- Optimized images with Optimole
- Removed 12 unnecessary plugins
Result: Load time improved by 300% (down to 2.1 seconds), and conversion rates increased by 28%.
Case Study 2: Content-Heavy Blog
A popular blog with thousands of posts was experiencing slow loading and high bounce rates. The optimization process included:
- Database optimization with WP-Optimize
- CDN implementation with Cloudflare
- Image optimization and lazy loading
- PHP upgrade from 7.4 to 8.1
Result: 68% improvement in average load times and a 35% increase in organic traffic within 3 months.
WordPress Performance Optimization: Your Action Plan
Feeling overwhelmed? Don’t worry. You don’t need to implement everything at once. Here’s a prioritized action plan:
Phase 1: Foundation (Week 1)
- Evaluate and upgrade hosting if necessary
- Install and configure a caching plugin
- Audit and remove unnecessary plugins
- Optimize existing images
Phase 2: Enhancement (Week 2)
- Implement a CDN
- Optimize database
- Enable GZIP compression
- Minify CSS and JavaScript
Phase 3: Fine-Tuning (Week 3+)
- Address Core Web Vitals issues
- Implement preloading strategies
- Set up performance monitoring
- Consider advanced optimizations
Maintenance (Ongoing)
- Monitor performance weekly
- Update WordPress, themes, and plugins regularly
- Review and optimize new content
- Clean database monthly
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Before you start optimizing, here are the biggest mistakes I see people make:
- Installing Multiple Caching Plugins: This creates conflicts, not speed
- Over-Optimizing: Sometimes aggressive optimization breaks functionality
- Ignoring Mobile Performance: Over 60% of traffic is mobile—optimize for it
- Not Testing Changes: Always test optimizations on a staging site first
- Focusing Only on Plugin Solutions: Hosting quality matters more than any plugin
The Bottom Line: Speed Equals Success
WordPress performance optimization isn’t just about making your site faster—it’s about making your business more successful. Every second you shave off your load time translates to better user experience, higher search rankings, and increased conversions.
The techniques in this guide have been proven to work across thousands of WordPress sites. Some are quick wins you can implement today, while others require more planning and effort. But here’s the thing: your competitors are probably not doing this stuff. That gives you a massive advantage.
Start with the basics—hosting, caching, and image optimization—then work your way through the advanced techniques. Don’t try to do everything at once, but don’t wait for the perfect moment either. Every day your site loads slowly is money left on the table.
Your users (and your bank account) will thank you for it.
Ready to Supercharge Your WordPress Site?
Performance optimization can seem daunting, but you don’t have to do it alone. If you need help implementing these strategies or want a professional performance audit of your WordPress site, we’re here to help. After all, we’ve been optimizing WordPress sites since before it was cool. And we love helping businesses unlock their site’s true potential.